References
1. 2020 Alzheimer’s disease facts and figures. Alzheimers Dement. 2020;10.1002/alz.12068. doi:10.1002/alz.12068
2. Onyike CU, Diehl-Schmid J. The epidemiology of frontotemporal dementia. Int Rev Psychiatry. 2013;25(2):130-137.
3. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Traumatic Brain Injury and Concussion. Published March 29, 2019. Accessed October 10, 2020. https://www.cdc.gov/traumaticbraininjury/data/tbi-ed-visits.html
4. Mendez MF, Paholpak P, Lin A, Zhang JY, Teng E. Prevalence of traumatic brain injury in early versus late-onset Alzheimer’s disease. J Alzheimers Dis. 2015;47(4):985-993.
5. Bigler ED. Traumatic brain injury, neuroimaging, and neurodegeneration. Front Hum Neurosci. 2013;7:395.
6. Desikan RS, Rafii MS, Brewer JB, Hess CP. An expanded role for neuroimaging in the evaluation of memory impairment. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2013;34(11):2075-2082.
7. Jack CR Jr, Bennett DA, Blennow K, et al. NIA-AA research framework: toward a biological definition of Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dement. 2018;14(4):535-562.
8. Palmqvist S, Janelidze S, Quiroz YT, et al. Discriminative accuracy of plasma phospho-tau217 for Alzheimer disease vs other neurodegenerative disorders. JAMA. 2020;324(8):772-781.
9. Mendez MF. The accurate diagnosis of early-onset dementia. Int J Psychiatry Med. 2006;36(4):401-412.
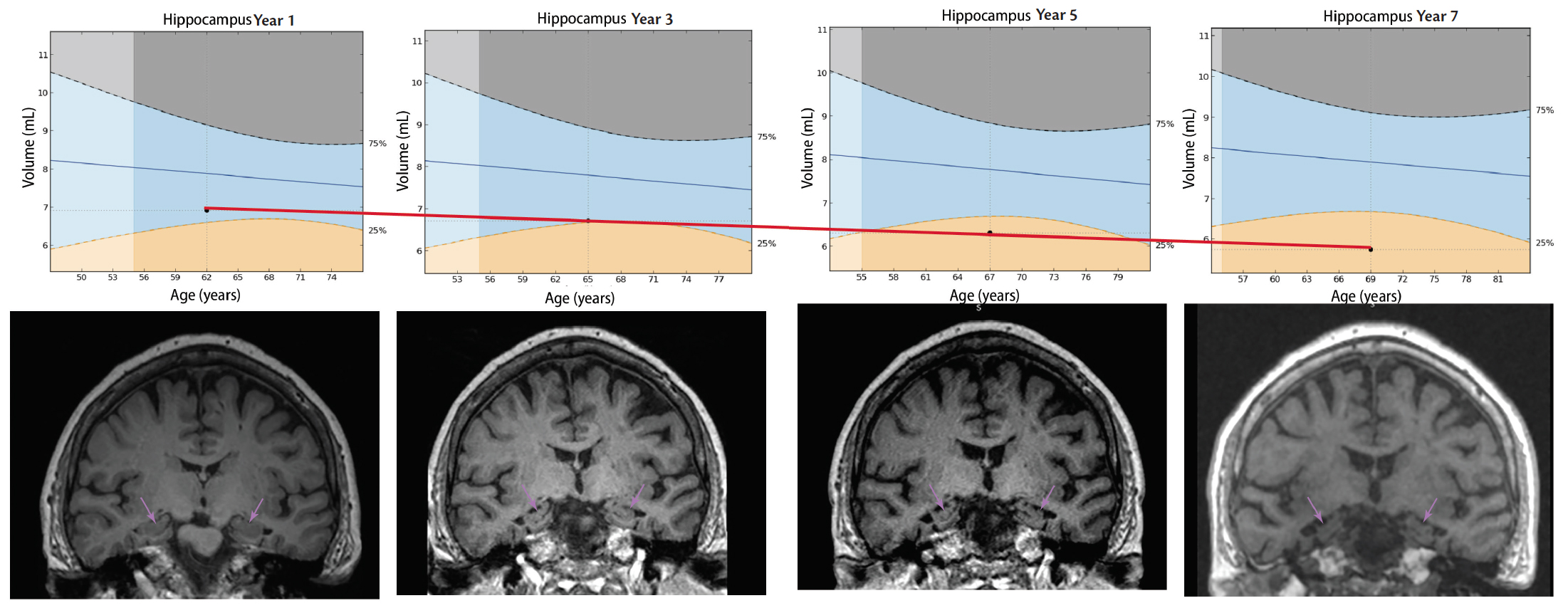
10. Raji CA, Lopez OL, Kuller LH, Carmichael OT, Becker JT. Age, Alzheimer disease, and brain structure. Neurology. 2009;73(22):1899-1905.
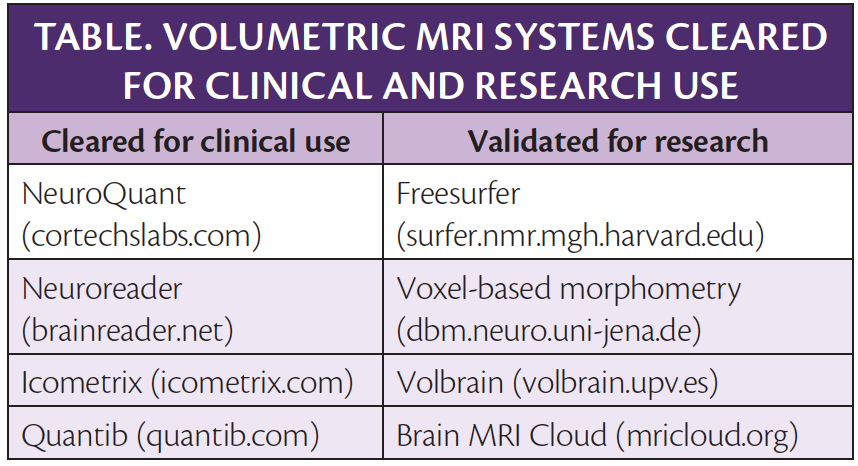
11. Brewer JB. Fully-automated volumetric MRI with normative ranges: translation to clinical practice. Behav Neurol. 2009;21(1):21-28.
12. Ahdidan J, Raji CA, DeYoe EA, et al. Quantitative neuroimaging software for clinical assessment of hippocampal volumes on MR imaging. J Alzheimers Dis. 2016;49(3):723-732.
13. Struyfs H, Sima DM, Wittens M, et al. Automated MRI volumetry as a diagnostic tool for Alzheimer’s disease: Validation of icobrain dm. Neuroimage Clin. 2020;26:102243. doi:10.1016/j.nicl.2020.102243
14. Hofman A, Brusselle GG, Darwish Murad S, et al. The Rotterdam study: 2016 objectives and design update. Eur J Epidemiol. 2015;30(8):661-708.
15. Mettenburg JM, Branstetter BF, Wiley CA, Lee P, Richardson RM. Improved detection of subtle mesial temporal sclerosis: validation of a commercially available software for automated segmentation of hippocampal volume. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2019;40(3):440-445.
16. Zarow C, Wang L, Chui HC, Weiner MW, Csernansky JG. MRI shows more severe hippocampal atrophy and shape deformation in hippocampal sclerosis than in Alzheimer’s disease. Int J Alzheimers Dis. 2011;2011:483972. doi:10.4061/2011/483972
17. Manjón JV, Coupé P. volBrain: an online MRI brain volumetry system. Front Neuroinform. 2016;10:30.
18. Shinagawa S, Catindig JA, Block NR, Miller BL, Rankin KP. When a little knowledge can be dangerous: false-positive diagnosis of behavioral variant frontotemporal dementia among community clinicians. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord. 2016;41(1-2):99-108.
19. McCarthy J, Collins DL, Ducharme S. Morphometric MRI as a diagnostic biomarker of frontotemporal dementia: A systematic review to determine clinical applicability. Neuroimage Clin. 2018;20:685-696.
20. Rohrer JD. Structural brain imaging in frontotemporal dementia. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012;1822(3):325-332.
21. Ross DE, Ochs AL, Seabaugh JM, Shrader CR; Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative. Man versus machine: comparison of radiologists’ interpretations and NeuroQuant volumetric analyses of brain MRIs in patients with traumatic brain injury. J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2013;25(1):32-39.
22. Ross DE, Ochs AL, DeSmit ME, Seabaugh JM, Havranek MD; Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative. Man versus machine part 2: comparison of radiologists’ interpretations and NeuroQuant measures of brain asymmetry and progressive atrophy in patients with traumatic brain injury. J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2015;27(2):147-152.
23. Barrio JR, Small GW, Wong KP, et al. In vivo characterization of chronic traumatic encephalopathy using [F-18]FDDNP PET brain imaging [published correction appears in Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015 Jun 2;112(22):E2981]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015;112(16):E2039-E2047. doi:10.1073/pnas.140995211
24. Raji CA, Merrill DA, Barrio JR, Omalu B, Small GW. Progressive focal gray matter volume loss in a former high school football player: a possible magnetic resonance imaging volumetric signature for chronic traumatic encephalopathy. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2016;24(10):784-790.
25. Meysami S, Raji CA, Merrill DA, Porter VR, Mendez MF. MRI volumetric quantification in persons with a history of traumatic brain injury and cognitive impairment. J Alzheimers Dis. 2019;72(1):293-300.